|
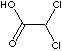
DICHLOROACETIC ACID |
| 2,2-Dichloroacetic acid; Bichloracetic acid; Dichlorethanoic acid; Dichloroethanoic acid; Kyselina dichloroctova; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
79-43-6; 42428-47-7 |
|
EINECS RN |
201-207-0 |
|
FORMULA |
Cl2CHCOOH |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
128.94 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
colourless to slightly yellowish liquid |
|
MELTING POINT |
9 - 11 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
194 C |
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Miscible |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
112 C |
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. May decompose upon hearting |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, Hydrogen chloride, phosgene. |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Instability: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Causes severe eye and skin burns. Causes severe digestive and respiratory tract burns. Very toxic to aquatic organisms. Target Organs: Blood, kidneys, liver, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, eyes, skin. |
|
EYE |
Causes eye burns. |
|
SKIN |
Causes skin burns. May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. |
|
INGESTION |
Causes gastrointestinal tract burns. May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
Causes chemical burns to the respiratory tract. May be harmful if inhaled. |
|
CHRONIC |
May cause liver and kidney damage. Adverse reproductive effects have been reported in animals. Laboratory experiments have resulted in mutagenic effects. Chronic exposure may cause blood effects. Animal studies have reported the development of tumors. |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
1764 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
8 |
| PACKING GROUP |
II |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
C N |
|
RISK PHRASES |
35-50 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-45-61 |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION |
|
Monochloroacetic acid, chlorinated simplest carboxylic acid, has electron-withdrawing atoms on the next carbon to acid. Alha-chlorine makes monochloroacetic acid more acidic than acetic acid. The more electronegative atom presence tends to strengthen the acidic property. Trichloroacetic acid is stronger than monochloroacetic acid. Trichloroacetic acid is a corrosive and toxic crystals, with pungent odour; boiling point 198 C and melting point 58 C. It is soluble in water and the solution is a strong acid. Trichloroacetic acid can be used as a useful chemical intermediate for the production of various target molecules (medicine, pharmacy, and herbicides). The sodium salt is used as a weedkiller directly. It is used as reagent for albumin detection. Dichloroacetic acid is a colourless to slightly yellowish liquid, highly corrosive. It is miscible with water and is readily soluble in alcohols, ketones, hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons. It is typically prepared by the reduction of trichloroacetic acid. It has shows the weaker acidity than benzenesulphonic acid or trichloroacetic acid, which provides milder reaction conditions for detritylation in the oligonucleotide synthesis and more stability against decomposition to hydrochloric acid. It is used as an intermediate in the production of glyoxylic acid, dialkoxy and diaroxy acids, and sulfonamides. Some end products include chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol. It is used in preparations of iron chelates for agricultural industry. It is used to a lesser extent as a cauterizing agent in dermatology. |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
colourless to slightly yellowish liquid |
|
DICHLOROACETIC ACID |
98.0% max |
|
MONOCHLOROACETIC ACID |
0.5% max |
|
TRICHLOROACETIC ACID |
1.0% max |
|
WATER |
0.5% max |